It is water-soluble and binds with impurities to make them water-soluble. It is available either as a liquid or a powder. Detergents are used to clean clothes and dishes. They are amphiphilic, i.e.; they have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions present. Usually, detergents are alkylbenzene sulfonates. Unlike Soap, their solubility increases in hard water. This is because the sulfonate group present in the detergent doesn’t combine with calcium or other ions in hard water. While the carboxylate group in soaps readily forms bonds with calcium. In this article, we’ll address the question of whether detergent is an acid or a base? So, is detergent an acid or a base? Detergents are basic in nature. This is because the chemical compounds like anionic groups, long-chain hydrocarbons, and a single non-ionic group used to prepare a detergent are basic. On a pH scale, detergents stand at 10. Most impurities are acids. Hence, a basic detergent will be an excellent cleaner for them.
The pH of a detergent
On a pH scale, acid to base runs 1 to 14 wherein compounds ranging from 1 to 6 are marked as acids while those ranging between 8 to 14 are termed as bases. Neutral compounds are denoted by 7. Detergents are compounds of sodium or potassium hydroxides. On a pH scale, substances that form compounds with potassium or sodium hydroxides fall between 10 to 14. This makes them a basic compound. Hence, detergents are basic. Generally, detergents stand 10 on the pH scale. While detergents with ammonia stand towards 12 on the scale and have bleaching properties.
Why is Detergent a Base?
Since detergents are compounds of sodium or potassium hydroxides, we’ll understand why sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a base using the following theories: • According to Arrhenius’s theory, when a substance dissociates in water to generate OH- ions, it’s a base. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) when dissolved in water dissociates to Na+ (cations) and OH- (anions). The chemical reaction for the same is given below: NaOH + H2O —–> Na+ + OH- + H2O + heat • According to the Bronsted Lowry theory, a base is a proton (H+ ion) acceptor that forms a conjugate acid. It’s known as a Bronsted Lowry base. While acid is a proton donor that forms a conjugate base. It’s known as Bronsted Lowry acid. The chemical reaction for the same is as follows: NaOH (base) + HCl (acid) —-> H2O (conjugate acid) + NaCl (conjugate base) • According to the Lewis theory, a base is an electron-pair donor and is called a Lewis base. While acid is an electron-pair acceptor and is called a Lewis acid. Sodium hydroxide is a Lewis base because the lone pairs on its OH- ions can be donated to a Lewis acid to form a new compound.
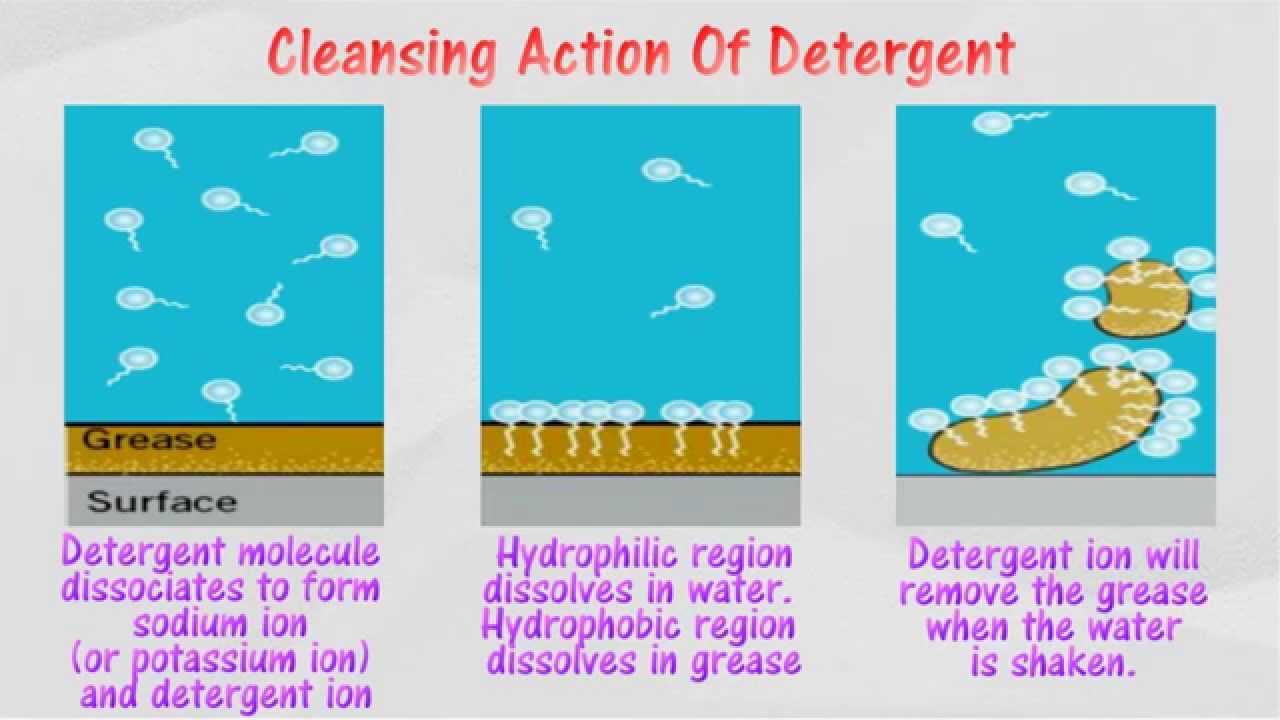
How Does a Detergent Work?
Detergents are made from long-chain molecules that have a head and a tail. Each of these molecules is known as a surfactant. The head of the surfactant is the hydrophilic end. Hence, it navigates towards the water. While the tail of the surfactant is the hydrophobic end. Thus, it navigates away from the water and binds to the surface of impurities. When detergent is added to clothes soaked in water, the tails of the surfactants bind with the impurities while the heads remain in the water. The attractive forces between the water and the hydrophilic end (head) are strong enough to lift and withdraw away impurities from the clothes. The blob of oil gets surrounded by surfactants and gets broken down by them into smaller pieces. These pieces are washed away by the water and the cloth becomes free from impurities and dirt. Also, detergents reinforce the washing process by decreasing the surface tension of water. Surface tension helps the water layer on its surface to maintain its structure and not spread out. Reduced surface tension will assist in navigating the extracted dirt away from the clothes and avoid its saturation near the surface of the clothes.
Components of a Detergent
A detergent has different ingredients with a specific role to play. These ingredients are as follows: • Builders: Builders are pivotal components that form the base of detergents. They improve the efficiency of surfactants and prevent mineral precipitation. They break out fats into small washable globules. Sodium silicate, a type of builder, is safe to use because it nullifies the corrosive effects of detergent. Alkaline builders are water-soluble salts that neutralize acids. This assists in stain removal. • Surfactants: Surfactants, also known as foamers, boost the washing ability of detergents. They assist in forming and breaking down stains. Anionic surfactants don’t work well in hard water and need the assistance of non-ionic surfactants to leverage the cleansing action of the detergent. • Enzymes: Different enzymes target specific impurities and wash them out. They help in shortening the time required to cleanse your clothes even at lower temperatures. Proteases, lipases, and amylases are a few enzymes used in detergents. • Optical brighteners: Optical brightness absorbs UV light and reflects visible light. This helps in boosting the whiteness and brightness of your clothes. • Colorful speckles: Color speckles are brightening agents that help maintain the vibrance of your clothes.
Types of Detergents
There are four main types of detergents available based on the type of surfactant it has. These include: • Anionic detergents: In an anionic detergent a lipophilic hydrocarbon group forms the anion of the detergent. • Cationic detergents: Cationic detergents are also known as “invert soaps”. The surface-active part (surfactant) of the detergent is a cation instead of an anion in this case. • Non-ionic detergents: Non-ionic detergents, as the name suggests, don’t have an anionic or cationic hydrophilic group. • Amphoteric detergents: Amphoteric detergents have both anionic and cationic hydrophilic groups present on their long-chain molecules.
Difference between an acid and a base?
Acids generate H+ ions when dissolved in water. While bases generate OH- ions when dissolved in water. Acids have a sour flavor while bases have a bitter flavor. For acids, the pH range is between 1 to 7. But for bases, the pH range is between 7 to 14. The strength of an acid pivots on its H+ ion concentration while the strength of a base depends on its OH- ion concentration. Acids convert blue litmus paper to red. While bases convert red litmus paper to blue. Acids are used in car batteries and carbonated drinks. While bases are used in soap and detergent production. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is an acid while sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a base.
What is the difference between a detergent and a soap?
Soaps are made from natural ingredients like plant oils or animal fatty acids. While detergents are man-made and synthetic derivatives of soap. Soaps have limited use but detergents cater to all sorts of our cleaning and washing requirements. This is because of the presence of a versatile ingredient called surfactant i.e., surface active agent.
Uses of Detergent
Detergents are known for their applications beyond cleaning. Some of which are listed below: • Primarily, detergents are used for cleaning laundry and dishwashing. • Apart from these, detergents can also be used to clean tiles, tubs, toilets, worktops, and floors. • Powdered detergent can be used to absorb oil spilled on the floor. • Detergents can increase water softness by reducing its surface tension. • Powdered detergents combat the growth of fungus within moist areas. • Detergents help in the crystallization process of membrane proteins. Also, they prevent non-specific binding. • In biology, detergents are used to facilitate processes like cell lysis, cell permeabilization, and gel electrophoresis. Is detergent soluble in water? Yes, detergents are soluble in water. Surfactants aggregate and form micelles that dissolve in water. Micelles are small groups of hydrophobic ends (tails) of the surfactant that assist in the removal of impurities from the surface of your clothes. Is detergent soluble in organic solvents? No, detergents aren’t soluble in organic solvents. This is because organic solvents are non-polar and hence, they can’t break down the ionic bonds present between the molecules of the detergent. Is washing powder an acid or a base? The pH of washing powder ranges between 6.5 to 8. This makes it a base. Hence, washing powder is basic in nature. Is soap an acid or a base? Soap is a mixture of a weak acid (fatty acids) and a strong base. This results in the formation of alkali salts. The pH of the soap solution is between 8 and 9. Hence, soap is a base. Why is detergent called soapless soap? Detergents are synthetic derivatives of petroleum. Unlike soaps, detergents don’t produce lather nor do they contain chemicals like sodium stearate. Hence, they’re called soapless soaps. Is detergent an organic compound? Yes, detergents are organic compounds. This is because they contain carbon-carbon bonds. Related posts you must read Is NH3 an Acid or Base KNO3 Acid or Base Is Bleach an Acid or Base Is Baking Soda Acidic or Basic Is NH4Br Acid or Base NaCN Acid or Base KNO3 Acid or Base Is NH4 an Acid or Base Is NH4Cl Acid or Base pH of Alcohol
Conclusion
Detergents are a group of surfactants that speed up the cleaning process of clothes and dishes. They’re amphiphilic and water-soluble. Detergents have a pH between 10 to 14. Hence, they’re bases. There are four types of detergents namely anionic, cationic, non-ionic, and amphoteric. The hydrophobic end of the molecule sticks to the surface of impurities while the hydrophilic ends pull them away from the surface of your clothes.