It is corrosive to metals and also, causes irritation to the eyes and skin of humans. It exists in monomeric as well as polymeric form. It is also considered the most important sulfur oxide, economically. It is used in the manufacturing of paints, in electrical equipment, in water treatment, in building and construction material, in air emission control, etc. Hello folks!! In this article, we will answer your queries related to sulfur trioxide. So keep reading…. Is SO3 covalent or ionic? Sulfur trioxide is a covalent compound. In the case of sulfur trioxide, the bonds are formed between the two non-metals i.e. sulfur and oxygen, and the electrons are shared between the participating atoms. Therefore, the bonds formed in this molecule are covalent in nature. However, the electronegativity of sulfur is 2.58 while that of oxygen is 3.44 due to which the electrons are not shared equally between the two atoms. This electronegativity difference results in the formation of polar covalent bonds, albeit, the molecule in itself is non-polar. We will study why and how in the coming sections.
What type of bond does SO3 contain?
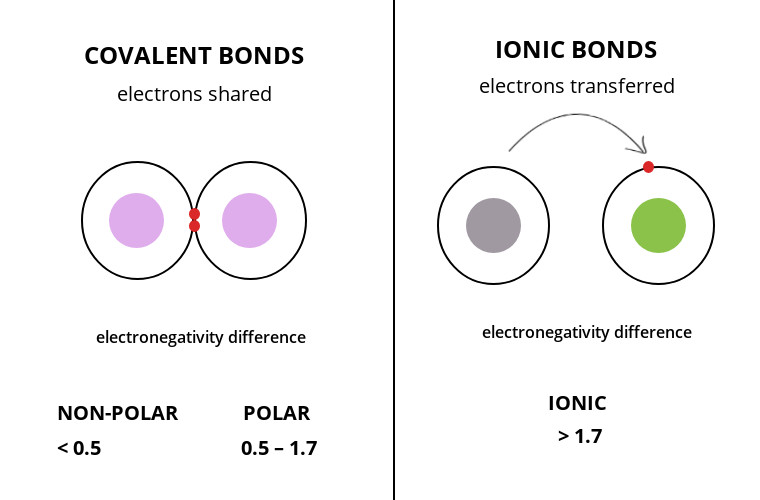
Before getting to the answer, we must first understand why atoms form bonds at all. Actually, every atom has a tendency to become stable. As the stability of an atom depends upon the number of electrons present in its valence shell, every atom tends to complete its octet. This is the reason for the bond formation. In a bond, the atoms gain, lose, or share their electrons depending upon their requirement. The ability of an atom to attract the electrons, shared in the formation of a bond, towards itself, is known as its electronegativity. The difference in the electronegativity of the two atoms participating in the bond formation decides the nature of the bond formed. Usually, the atoms in which the electronegativity difference is above 1.6 form an ionic bond, and the atoms having electronegativity difference below 1.6 form a covalent bond. However, the covalent bonds are further divided as polar and non-polar covalent bonds.
If the difference in the electronegativity of the bonding atoms is between 0.4 to 1.6, the bond forms is a polar covalent bond, while if the electronegativity difference is below 0.4, the bond is a non-polar covalent bond. In a polar covalent bond, the shared pair of electrons slightly shifts towards the atom having more electronegativity. Due to this, a partial negative charge develops on the more electronegative atom while a partial positive charge develops on the less electronegative atom. These charges are denoted using the symbol δ+, for partial positive, and δ-, for partial negative. On the other hand, in a non-polar covalent bond, the electrons are shared more or less equally between the two combining atoms. In the case of sulfur trioxide, the electronegativity of sulfur is 2.58 while, the electronegativity of oxygen is 3.44. Therefore, the electronegativity difference is around 0.86. As this difference lies between 0.4 and 1.6, the bonds formed in the SO3 molecule are polar covalent bonds. However, the net charge on the sulfur trioxide molecule is zero owing to its geometry, due to which the molecule in itself is non-polar. Keep reading to know more…
Why is SO3 a Covalent Molecule?
Usually, when a bond is formed between the two non-metals, it is a covalent bond. In the case of sulfur trioxide, both sulfur and oxygen are non-metals. Hence, the bond formed between these two atoms is covalent. Moreover, both sulfur and oxygen belong to group 16 of the periodic table and contain 6 valence electrons in their outermost shell. Thus, both these atoms require two electrons each to complete their octet. Further, the difference between the electronegativity of sulfur and oxygen lies below 1.6. As we have already studied in the earlier section, the ionic bonds are formed when the electronegativity difference is above 1.6 while covalent bonds are formed when it is below 1.6. Hence, it further indicates that the bonds formed between the oxygen and sulfur atoms in the SO3 molecule are covalent.
Covalent Vs. Ionic bond
Till now, we have studied a lot about why and how the covalent and ionic bonds are formed. In this section, we will study more about the difference between these two bonds. The atoms form bonds to stabilize themselves and a number of factors determine the nature and characteristics of the bond formed. Let us learn how: • As clear from the names, the ionic bonds involve the bond between ions, while the covalent bonds involve different atoms. • The ionic bonds are formed either between two metals, or a metal and a non-metal, or a metal and a polyatomic ion. On the other hand, the covalent bond is formed between the two non-metals. • The ionic compounds are formed when one atom donates its electron or electrons to another atom, while a covalent bond is formed when the electrons are shared between the participating atoms. • The ionic bonds are formed when the difference in the electronegativity of the atoms participating in the bond formation is greater than 1.6, while the covalent bonds are formed when the electronegativity difference is below 1.6. • The ionic bond is only of one type while the covalent bond can further be divided into polar and non-polar covalent bonds, based upon the difference in the electronegativity of the participating atom. When the difference in the electronegativity of the participating atoms lies between 0.4 and 1.6, polar covalent bonds are formed. However, if the electronegativity difference is below 0.4 non-polar covalent bonds are formed. • When the ionic compounds are dissolved in an aqueous solution, they usually result in the formation of a positive (cation) and a negative (anion) ion. On the other hand, the covalent compounds normally do not dissolve in water. • In general, ionic compounds are good conductors of heat and electricity while covalent compounds are bad conductors of heat and electricity. • The melting and boiling points of ionic compounds are usually higher in comparison to the covalent compounds. • The ionic compounds mostly occur as solids at room temperature, while covalent compounds occur as liquids or gases. • A few examples of ionic compounds are NaCl, NaCN, NH4Cl, etc., while a few examples of covalent compounds are SO3, H2O, etc.
Why is SO3 not Ionic?
As discussed in the previous section, ionic compounds are formed when the difference between the electronegativity of the two atoms involved in the bond formation is more than 1.6. Also, ionic bonds are formed when a metal atom bonds with another metal atom, a non-metal atom, or a polyatomic ion. In the case of sulfur trioxide, both the participating atoms i.e. oxygen and sulfur are non-metals, indicating that the bond formed between these two atoms cannot be ionic. Further, the electronegativity difference between these two atoms is below 1.6. Hence, sulfur trioxide is not an ionic compound. Related Topics Is NaCl Ionic or Covalent Is NH4Cl Ionic or Covalent Is H2O Ionic or Covalent Is MgO Ionic or Covalent Is PCl3 Ionic or Covalent Is CaF2 Ionic or Covalent Is H2S Ionic or Covalent Is AlCl3 Ionic or Covalent Is CO Ionic or Covalent Is CaO Ionic or Covalent
Is SO3 Polar or Non-polar?
So far we have discussed that the bonds formed between the sulfur atom and the oxygen atoms, in the sulfur trioxide molecule are covalent. We have also learned that the bond is polar in nature as the difference in the electronegativity of the sulfur and oxygen atom lies between 0.4 and 1.6. Therefore, the bond is termed a polar covalent bond. However, to your surprise, the SO3 molecule in itself is non-polar. Wondering how? Let me explain Actually, as per the VSEPR theory, the molecular geometry of the SO3 molecule is trigonal planar. Therefore, the SO3 molecule appears as follows:
As visible from the above figure, the three double bonds (S=O) between the sulfur and oxygen atoms are positioned at an angle of 120° from each other. Therefore, the polarity that arises in the S=O bonds, owing to the electronegativity difference between the two atoms, cancels out amongst each other. Hence, the overall polarity of the sulfur trioxide molecule becomes zero and the SO3 molecules become non-polar in nature.
Conclusion
• The sulfur trioxide molecule is covalent as both the participating atoms i.e. sulfur and oxygen are non-metals. • The difference in the electronegativity of the sulfur and oxygen atom is between 0.4 and 1.6. Therefore, the bond is polar covalent. • The SO3 molecule is non-polar as the geometry of sulfur trioxide is trigonal planar and the three S = O bonds lie at an angle of 120° from each other. Thus, the polarity of the bonds cancels amongst themselves.